| 产品名称 | BMM mach-1 多功能摩擦磨损测试仪,摩擦系数摩擦力测试仪 |
| 品牌 | 加拿大BMM |
| 产品货号 | mach-1 |
| 产品价格 | 现货询价 |
| 联系人 | 李先生 |
| 联系电话 | 18618101725 |
BMM mach-1 多功能摩擦磨损测试仪 |
|
| 该BMM mach-1 多功能摩擦磨损测试仪使用BMM 开发的软件使用垂直平台施加法向力,而其他平台施加旋转或平移运动,您可以轻松确定测试中涉及的摩擦系数和力。摩擦测试的目的涵盖了广泛的兴趣领域。例如,测试一种新型润滑剂的有效性或比较两个样品的表面te性。 | |
| 该系统可模块化集成摩擦磨损、压痕、拉伸、压缩、三弯曲、四点弯曲、扭力、剪切、摩擦磨损、3D轮廓表面形貌表征、电te性等各种力电多物理场测试。 能对ji软、ji硬组织材料进行精密可靠的机械刺激和表征。允许表征的机械性能包括刚度、强度、模量、粘弹性、塑性、硬度、附着力、肿胀和松弛位移控制运动各种机械te性。 | |
|
点击查看 该系统多功能多组织材料各种力-电te性测试介绍 |
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
摩擦
摩擦测试确定两个表面在受到接触力时相互滑动的难易程度。在这些测试中通常观察到两种主要现象:静摩擦和动摩擦。静摩擦力是阻止物体从静止状态移动的力,而动摩擦力是在两个表面已经运动时作用于它们之间的力。BMM 开发的软件使用垂直平台施加法向力,而其他平台施加旋转或平移运动,您可以轻松确定测试中涉及的摩擦系数和力。摩擦测试的目的涵盖了广泛的兴趣领域。例如,测试一种新型润滑剂的有效性或比较两个样品的表面te性。
|
|
|
特点亮点 1、适用样品范围广: 1.1、从骨等硬组织材料到脑组织、眼护等骨组织材料 1.2、从粗椎间盘的样品到j细纤维丝 2、通高量压痕测试分析 ◆样品范围广:ji软脑组织泡沫到陶瓷、金属 ◆模量范围广3pa到670Gpa ◆wu需表面平坦,可在不规则表面压痕(刚度、硬度、厚度、表面轮廓等测试) ◆压痕不要求压缩轴垂直于样品表面对齐 ◆可模块化集成多轴向多功能多材料:可集成3D轮廓表面形貌表征、拉伸、压缩、三弯曲、四点弯曲、扭力、剪切、摩擦磨损、电te性等各种力电多物理场测试。 ◆压痕同时可测量厚度信息 ◆红宝石压头,坚固不易断,使用成本低 ◆样品不需要从组织中收集 ◆组织的破坏小 ◆维持被测材料的机械环境及其与周围材料的相互作用 ◆自动mapping ◆亚微米分辨率
◆一台仪器即可进行从纳米到宏观尺度的压痕 ◆可以在将样品浸入溶液中的情况下进行 3、力学类型测试分析功能齐:张力,剪切,摩擦,扭转,摩擦和2d/3d压痕,3d表面,3d厚度,粘合,塔接塔接合力等各力学类型支持,微观结构支持,微观微观表征及动词力学分析研究 4、高精度高分辨率: 4.1、位移尺寸达0.1um 4.2、力达0.025mN 5、行程范围广:50-250mm 6、气质、可携带容器内 7、高变观察追踪分析 八款精品、多款、多力精品 9、活性组织分布测试分析 10、产品种类,文献量达上千篇
4、多力偶联测试,如测量旋转中两个软骨表面之间的摩擦系数
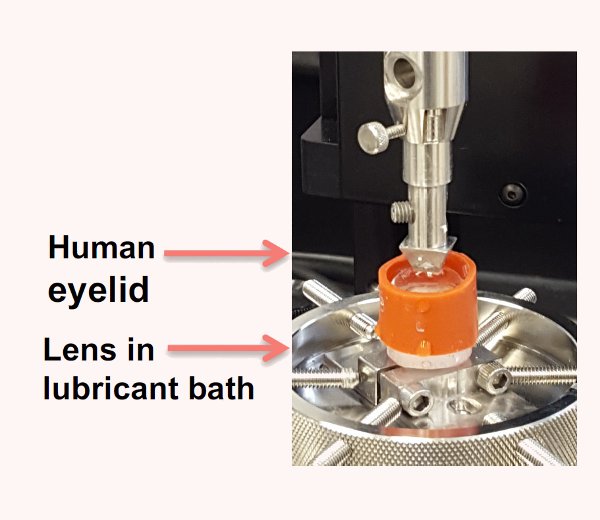
5、微力测试隐形眼睛摩擦测试
|
|
BMM 摩擦磨损相关文献案例
Introduction: During daily physical activities, joint articulation results in 3-10% compression in its overall thickness. There is also consensus that articulation is a combined process of shearing and sliding, with relative rotational and translational motions between femoral condyle and tibia cartilage at least at the millimeter scale 2,3. The macroscale motions in the joint which translates...Read More Development of a Sequence of Mechanical Tests for Articular Cartilage at a Single LocationSim S, Chartrand A, Lavallee AP, Tessier J, Garon M, Quenneville E and Buschmann MDOrthopeadic Research Society Annual Meeting in Orlando, 2016
In a recent study, our group has highlighted the importance of considering the natural topographic variability of the mechanical properties over the articular surface, particularly in the context of cartilage repair, where it can screen the effect of a treatment [1]. Moreover, the availability of test sample is limited in those repair studies since the regions of interest are often limited in size....Read More
ASTM D1894 - Standard Test Method for Static and Kinetic Coefficients of Friction of Plastic Film and SheetingASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2014, www.astm.org
Significance and Use
4.1 Measurements of frictional properties may be made on a film or sheeting specimen when sliding over itself or over another substance. The coefficients of friction are related to the slip properties of plastic films that are of wide interest in packaging applications. These methods yield empirical data for control purposes in film production. Correlation...Read More
ASTM F1538 - Standard Specification for Glass and Glass Ceramic Biomaterials for ImplantationASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2009, www.astm.org
Abstract
This specification covers the material requirements and characterization techniques for glass and glass-ceramic biomaterials intended for use as bulk porous or powdered surgical implants, or as coatings on surgical devices, but not including drug delivery systems. Glass and glass-ceramic biomaterials should be evaluated thoroughly for biocompatibility before human use....Read More
ASTM F2451-05 - Standard Guide for in vivo Assessment of Implantable Devices Intended to Repair or Regenerate Articular CartilageASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2010, www.astm.org
Significance and Use
This guide is aimed at providing a range of in vivo models to aid in preclinical research and development of tissue engineered medical products intended for the clinical repair or regeneration of articular cartilage.
This guide includes a description of the animal models, surgical considerations, and tissue processing as well as the qualitative and quantitative...Read More
Mach-1 - Friction Testing on a Cartilage Disk or an Osteochondral Core (MA056-SOP08-D v2)Chartrand A and Quenneville EBMM Inc. Laval (QC), Canada, Effective Date: August 24th, 2015
Purpose
This procedure describes a standard method to realize a friction test on a cartilage disk or an osteochondral core using the Mach-1 TM mechanical tester.
Scope
This procedure can be used for the ex vivo friction test using a planar sliding method on a cartilage disk or an osteochondral core. It is highly...Read More
Mach-1 Analysis - Extraction of Mechanical Parameters Following Friction Testing on a Cartilage Disk or an Osteochondral Core (SW186-SOP07-D v2)Chartrand A and Quenneville EBMM Inc. Laval (QC), Canada, Effective Date: August 24h, 2015
Purpose
This procedure describes a MatLab-based method to extract mechanical parameters from the Mach-1 result files generated following friction testing on a cartilage disk or an osteochondral core as per MA056-SOP08-D.
Scope
This procedure based on a MatLab code can be applied using any Mach-1 result file obtained following a planar friction test of...Read More
Tailoring hydrogel surface properties to modulate cellular response to shear loadingMeinert C, Schrobback K, Levett PA, Lutton C, Sah R and Klein TJActa biomaterialia, October 2016. DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.10.011
Biological tissues at articulating surfaces, such as articular cartilage, typically have remarkable low-friction properties that limit tissue shear during movement. However, these frictional properties change with trauma, aging, and disease, resulting in an altered mechanical state within the tissues. Yet, it remains unclear how these surface changes affect the behaviour of embedded cells when the...Read More
Mechanical characterization of matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation (MACI®) grafts in an equine model at 53 weeksGriffin DJ, Bonnevie ED, Lachowsky DJ, Hart JC, Sparks HD, Moran N and Bonassar LJJournal of biomechanics, 48(10), 1944-1949. (2015)
There has been much interest in using autologous chondrocytes in combination with scaffold materials to aid in cartilage repair. In the present study, a total of 27 animals were used to compare the performance of matrix-assisted chondrocyte implantation (MACIs) using a collagen sponge as a chondrocyte delivery vehicle, the sponge membrane alone, and empty controls. A total of three distinct types of...Read More
Effect of synovial fluid on boundary lubrication of articular cartilageSchmidt TA and Sah RLOsteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007 Jan;15(1):35-47. Epub 2006 Jul 21
OBJECTIVES: The lubrication of articulating cartilage surfaces in joints occurs through several distinct modes. In the boundary mode of lubrication, load is supported by surface-to-surface contact, a feature that makes this mode particularly important for maintenance of the normally pristine articular surface. A boundary mode of lubrication is indicated by a kinetic friction coefficient...Read More
Combined Mechanical Characterizations Increases Sensitivity in the Assessment of Human Cartilage DegenerationSim S, Hadjab I, Chevrolat L-A, Masse M, Tong AL, Lavigne P, Garon M, Quenneville E and Buschmann MDAccepted for a podium presentation at ORS 2017
Introduction: We published a recent study showing superior sensitivity of electromechanical and indentation (instantaneous response) assessments versus well-established techniques, including histological Mankin score, to characterize cartilage degeneration. This study aims to determine whether the combination of instantaneous, relaxation and equilibrium mechanical properties and friction...Read More
Evaluation of genipin for stabilization of decellularized porcine cartilageElder S, Pinheiro A, Young C, Smith P and Wright EJ Orthop Res. 2016 Nov 18. doi: 10.1002/jor.23483
Abstract
We speculate that an acellular osteochondral xenograft may be a good alternative to allografts for repair of focal articular cartilage lesions. In order to make a xenograft resistant to enzymatic degradation and to prevent a chronic immune response it may beneficial to stabilize it through crosslinking. The concept is analogous to treatment of porcine bioprosthetic heart...Read More
Biomechanics and MechanoBiology of Human Cartilage ArticulationHsu FH, Alonso E, Raleigh AR, Saleh AA, Masuda K, Lotz MK, Chen AC and Sah ROrthopeadic Research Society Annual Meeting, 2016, Orlando, USA, Poster abstract 1428
Introduction: During joint articulation, cartilage, particularly that near the articular surface, undergoes a complex combination of compression, shear, and sliding.1,2 In vitro analyses have focused on cartilage biomechanics in response to relative surface movement at a constant velocity after startup. However, joint movement typically involves variability in the relative surface velocity....Read More
Composite hydrogel: A high fidelity soft tissue mimic for surgeryTan, Z., Dini, D., Rodriguez y Baena, F., & Forte, A. E.Materials & Design, 160, 886894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2018.10.018
Accurate tissue phantoms are difficult to design due to the complex non-linear viscoelastic properties of real soft tissues. A composite hydrogel, resulting from a mix of poly(vinyl) alcohol and phytagel, is able to reproduce the viscoelastic responses of different soft tissues due to its compositional tunability. The aim of this work is to demonstrate the flexibility of the composite hydrogel...Read More
The role of synovial fluid constituents in the lubrication of collagen-glycosaminoglycan scaffolds for cartilage repairAustyn R. Matheson, Eamon J. Sheehy, Gregory D. Jay, W. Michael Scott, Fergal J. O'Brien, Tannin A. SchmidtJournal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2021, 104445, ISSN 1751-6161, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2021.104445
Abstract
Extracellular matrix (ECM)-derived scaffolds have shown promise as tissue-engineered grafts for promoting cartilage repair. However, there has been a lack of focus on fine-tuning the frictional properties of scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering as well as understanding their interactions with synovial fluid constituents. Proteoglycan-4 (PRG4) and hyaluronan...Read More
Evaluation of in vitro contact lens friction: Effects of recombinant human proteoglycan 4 and test counterfaceChan, AmandaMaster thesis. University of Calgary, Calgary, AB. doi:10.11575/PRISM/5357 http://hdl.handle.net/1880/106276 |
|
点击查看 该系统多功能多组织材料各种力-电te性测试介绍 |
世联博研公司销售设备、租赁和承接实验技术服务一站式服务
我们世联博研公司专注生物力学、3D生物打印、再生医学、生物医学工程、微流控&组织器官芯片、细胞微环境在内的等生命科学国际前沿产品与技术引进中国,为中国科研学者提供专业、实效的仪器设备、耗材、试剂以及科研技术服务一站式解决方案:
●国际标准技术高度可控
●遵守标准的操作程序
●可靠的测试协议标准
●符合良好实验室规范准确数据分析报告